
Integration Point: Initialization
Gabriel Potvin
March 07, 2026
IntegrationPointInitialization.RmdGo back to the Getting Started: Overview page
Description
The Initialization integration point allows you to specify an optional function that will run before any other user-defined functions during simulations. This function can serve various purposes, such as:
- Setting a seed for reproducibility in the R environment.
- Loading required R packages or libraries.
- Setting global variables.
- Setting the working directory.
- Sourcing an additional file.
- Performing other initial setup tasks.
Availability
East Horizon Explore
This integration point is available in East Horizon Explore for the following study objectives and endpoint types:
| Time to Event | Binary | Continuous | Continuous with repeated measures | Count | Composite | Dual TTE-TTE | Dual TTE-Binary | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Two Arm Confirmatory | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Multiple Arm Confirmatory | 🔜 | ✅ | ✅ | - | - | - | - | - |
| Dose Finding | - | - | ❌ | - | - | - | - | - |
Legend
| Icon | Meaning |
|---|---|
| ✅ | Available |
| ❌ | Not available |
| 🔜 | Coming soon |
East Horizon Design
Click to expand/collapse
This integration point is available in East Horizon Design for the following study objectives and endpoint types:
| Time to Event | Binary | Continuous | Continuous with repeated measures | Count | Composite | Dual TTE-TTE | Dual TTE-Binary | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Two Arm Confirmatory | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | 🔜 | 🔜 |
| Two Arm Confirmatory - Multiple Endpoints | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | - | - | - | - | - |
| Multiple Arm Confirmatory | 🔜 | 🔜 | 🔜 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Dose Finding | - | - | ❌ | - | - | - | - | - |
This integration point is available in East Horizon Design for the following tests:
| Test | Study Objective | Endpoint | Availability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single Mean (One Arm Design) | One Arm Exploratory/Confirmatory | Continuous | ❌ |
| Mean of Paired Differences (Paired Design) | One Arm Exploratory/Confirmatory | Continuous | ❌ |
| Mean of paired Ratios (Paired Design) | One Arm Exploratory/Confirmatory | Continuous | ❌ |
| Single Proportion (One Arm Design) | One Arm Exploratory/Confirmatory | Binary | ❌ |
| Simon’s Two Stage (One Arm Design) | One Arm Exploratory/Confirmatory | Binary | ❌ |
| Logrank Weibull Distribution (One Arm Design) | One Arm Exploratory/Confirmatory | Time to Event | ❌ |
| Parametric Weibull Distribution (One Arm Design) | One Arm Exploratory/Confirmatory | Time to Event | ❌ |
| Logrank Exponential Distribution (One Arm Design) | One Arm Exploratory/Confirmatory | Time to Event | ❌ |
| Single Poisson Rate (One Arm Design) | One Arm Exploratory/Confirmatory | Count | ❌ |
| Difference of Means (Parallel Design) | Two Arm Confirmatory | Continuous | ✅ |
| Ratio of Means (Parallel Design) | Two Arm Confirmatory | Continuous | ❌ |
| Difference of Means (Crossover Design) | Two Arm Confirmatory | Continuous | ❌ |
| Ratio of Means (Crossover Design) | Two Arm Confirmatory | Continuous | ❌ |
| Difference of Proportions (Parallel Design) | Two Arm Confirmatory | Binary | ✅ |
| Ratio of Proportions (Parallel Design) | Two Arm Confirmatory | Binary | ✅ |
| Odds Ratio of Proportions (Parallel Design) | Two Arm Confirmatory | Binary | ✅ |
| Fisher’s Exact (Parallel Design) | Two Arm Confirmatory | Binary | ❌ |
| Logrank Test Given Accrual Duration and Accrual Rates (Parallel Design) | Two Arm Confirmatory | Time to Event | ✅ |
| Logrank Test Given Accrual Duration and Study Duration (Parallel Design) | Two Arm Confirmatory | Time to Event | ✅ |
| Logrank Test Given Accrual Duration and Accrual Rates (Population Enrichment) | Two Arm Confirmatory | Time to Event | ❌ |
| Ratio of Poisson Rates (Parallel Design) | Two Arm Confirmatory | Count | ❌ |
| Ratio of Negative Binomial Rates (Parallel Design) | Two Arm Confirmatory | Count | ❌ |
| Win Ratio (Parallel Design) | Two Arm Confirmatory | Composite | ❌ |
| MAMS Difference of Means (Pairwise Comparisons to Control) | Multiple Arm Confirmatory | Continuous | ✅ |
| MAMS Difference of Means: Combining P-Values (Pairwise Comparisons to Control) | Multiple Arm Confirmatory | Continuous | ✅ |
| MAMS Difference of Proportions (Pairwise Comparisons to Control) | Multiple Arm Confirmatory | Binary | ✅ |
| MAMS Difference of Proportions: Combining P-Values (Pairwise Comparisons to Control) | Multiple Arm Confirmatory | Binary | ✅ |
| MAMS Logrank (Pairwise Comparisons to Control) | Multiple Arm Confirmatory | Time to Event | 🔜 |
| MAMS Logrank: Combining P-Values (Pairwise Comparisons to Control) | Multiple Arm Confirmatory | Time to Event | 🔜 |
East
This integration point is available in East for the following tests (click to expand/collapse):
| Test | Number of Samples | Endpoint | Availability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Difference of Means (Parallel Design) | Two Samples | Continuous | ✅ |
| Difference of Proportions (Parallel Design) | Two Samples | Discrete | ✅ |
| Ratio of Proportions (Parallel Design) | Two Samples | Discrete | ✅ |
| Odds Ratio of Proportions (Parallel Design) | Two Samples | Discrete | ✅ |
| Logrank Test Given Accrual Duration and Accrual Rates (Parallel Design) | Two Samples | Survival | ✅ |
| Logrank Test Given Accrual Duration and Study Duration (Parallel Design) | Two Samples | Survival | ✅ |
| Chi-Square for Specified Proportions in C Categories (Single Arm Design) | Many Samples | Discrete | ✅ |
| Two Group Chi-Square for Proportions in C Categories (Parallel Design) | Many Samples | Discrete | ✅ |
| Multiple Looks - Combining P-Values (Pairwise Comparisons to Control - Difference of Means) | Many Samples | Continuous | ✅ |
| Multiple Looks - Combining P-Values (Multiple Pairwise Comparisons to Control - Difference of Proportions) | Many Samples | Discrete | ✅ |
| Multiple Looks - Combining P-Values (Pairwise Comparisons to Control - Logrank Test) | Many Samples | Survival | ✅ |
Instructions
In East Horizon (Explore and Design)
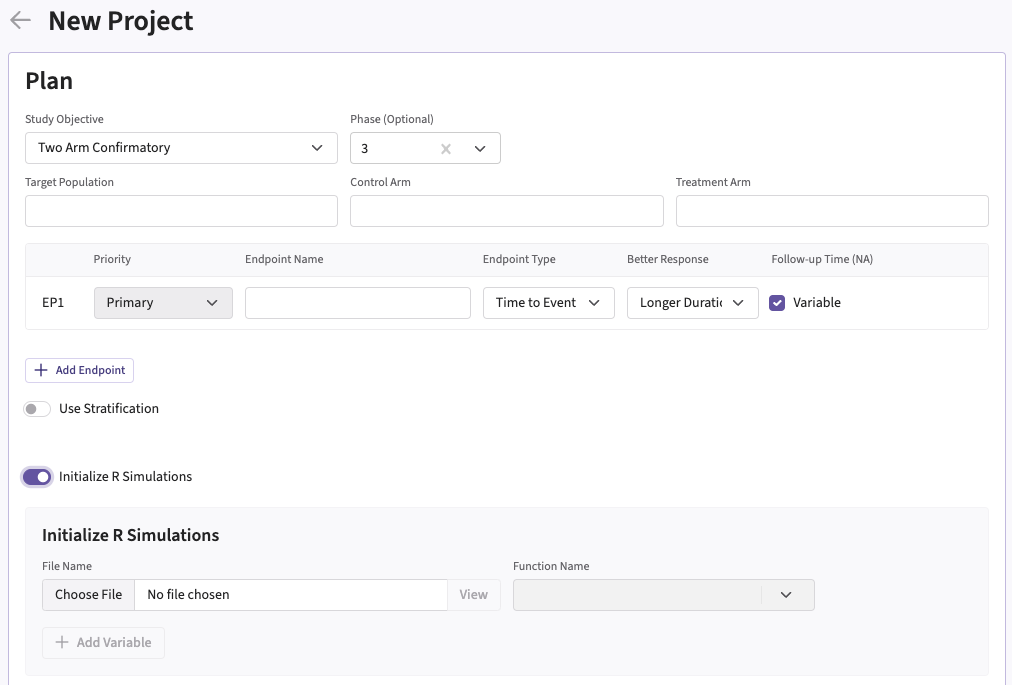
You can set up an initialization function when creating a new project by navigating to the Initialize R Simulations option under the Plan section.
Follow these steps (click to expand/collapse):
- Choose Initialize R Simulations in the Plan section when setting up a new Project.
- Turn on the switch to enable the feature.
- Browse and select the appropriate R file (
filename.r) from your computer, or use the built-in R Code Assistant to create one. This file should contain function(s) written to perform various tasks to be used throughout your Project. - Specify the function name you want to initialize. If the expected function is not displaying, then check your R code for errors.
- Set any required user parameters (variables) as needed for your function using + Add Variables.
- Continue creating your project.
For a visual guide of where to find the option, refer to the screenshot below:
In East
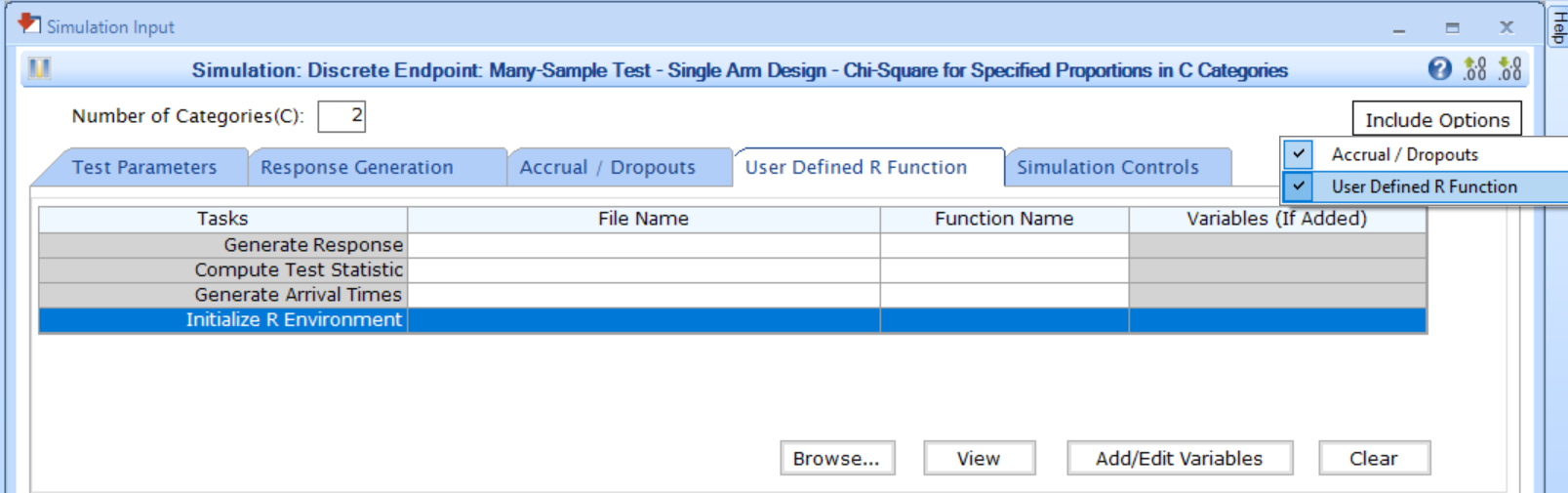
You can set up an initialization function by navigating to the Initialize R Environment task of the User Defined R Function tab of a Simulation Input window, after including the option. For some tests, the option will be available in the Treatment Selection tab.
Follow these steps (click to expand/collapse):
- Choose the appropriate test in the Design tab.
- If you see the Design Input window, compute the scenario using the Compute button, save the design using the Save in Workbook button, then navigate to the Simulation Input window by clicking on the Simulate Design button under Library.
- Click on the Include Options button on the top right corner of the Simulation Input window and select both Accrual / Dropouts and User Defined R Function.
- In the tab User Defined R Function, a list of tasks will appear. Place your cursor in the File Name field for the task Initialize R Environment.
- Click on the button Browse… to select the
appropriate R file (
filename.r) from your computer. This file should contain function(s) written to perform various tasks to be used throughout your Project. - Specify the function name you want to initialize. To copy the function’s name from the R script, click on the button View.
- Set any required user parameters (variables) as needed for your function using the button Add/Edit Variables.
- Continue setting up your project.
For a visual guide of where to find the option, refer to the screenshot below:
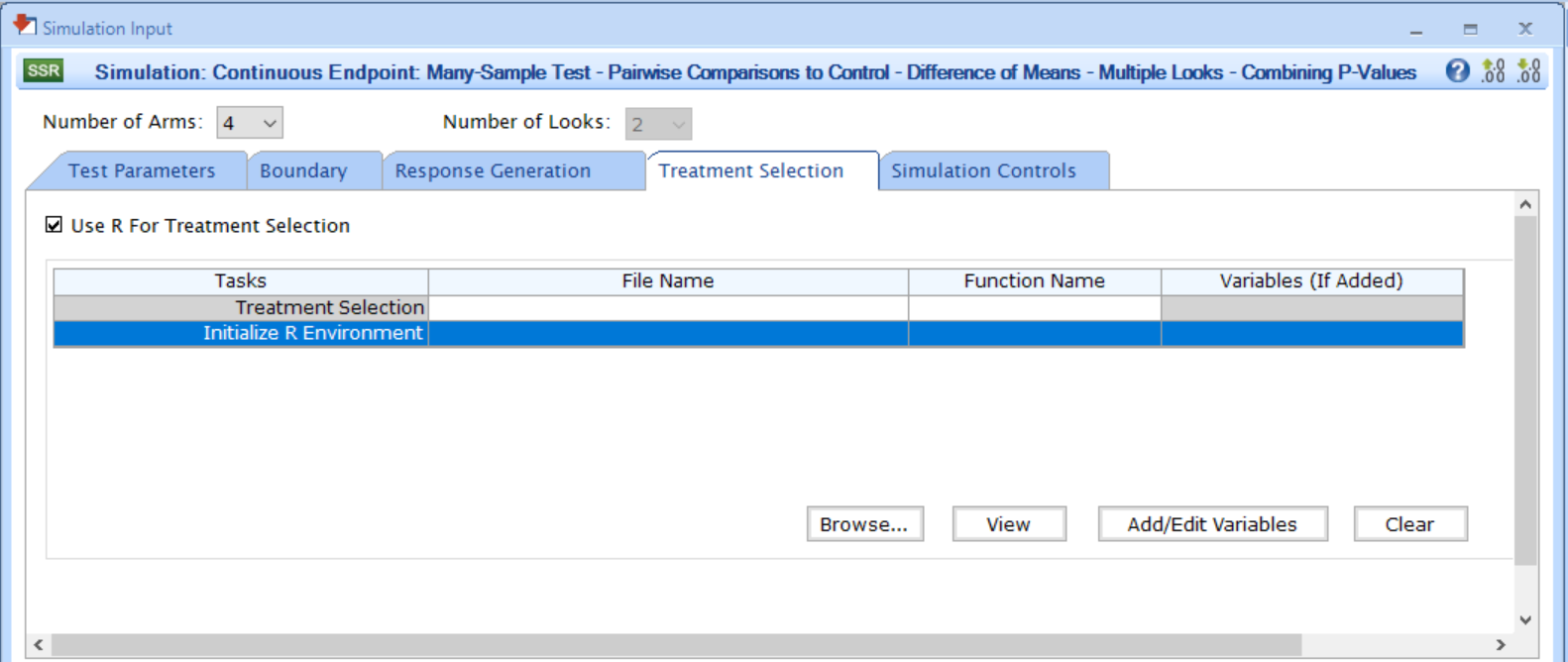
For the Multiple Looks - Combining P-Values (MAMS) tests, the option will be available when checking the box Use R for Treatment Selection in the Treatment Selection tab of the Simulation Input window. Refer to the screenshot below:
Input Variables
When creating a custom R script, you can optionally use certain
variables provided by East Horizon’s or East’s engine itself. These
variables are automatically available and do not need to be set by the
user, except for the UserParam variable. Refer to the table
below for the variable that is available for this integration point.
| Variable | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Seed | Integer | Randomization seed set by the engine. |
| UserParam | List | Contains all user-defined parameters specified in East Horizon’s or
East’s interface (refer to the Instructions
section). To access these parameters in your R code, use the syntax:
UserParam$NameOfTheVariable, replacing
NameOfTheVariable with the appropriate parameter name. |
Expected Output Variable
East Horizon expects an output of a specific type. Refer to the table below for the expected output for this integration point:
| Output | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ErrorCode | Integer | Optional. Can be used to handle errors in your script: – 0: No error.– Positive Integer: Nonfatal
error, the current simulation will be aborted, but the next simulation
will proceed.– Negative Integer: Fatal error, no
further simulations will be attempted. |
Minimal Template
Your R script could contain a function such as this one, with a name
of your choice. All input variables must be declared, even if they are
not used in the script. We recommend always declaring
UserParam as a default NULL value in the
function arguments, as this will ensure that the same function will work
regardless of whether the user has specified any custom parameters in
the interface.
A detailed template with step-by-step explanations is available here: Initialize.R
Init <- function( Seed = NULL, UserParam = NULL )
{
# Do something, for example set the seed
set.seed( 42 )
# If you want the user to set the seed using East Horizon's or East's interface, you could use set.seed( UserParam$seed )
# Error handling (no error)
nError <- 0
return( as.integer( nError ) )
}Examples
Used to load libraries in the following examples: